Access Point
Access Point
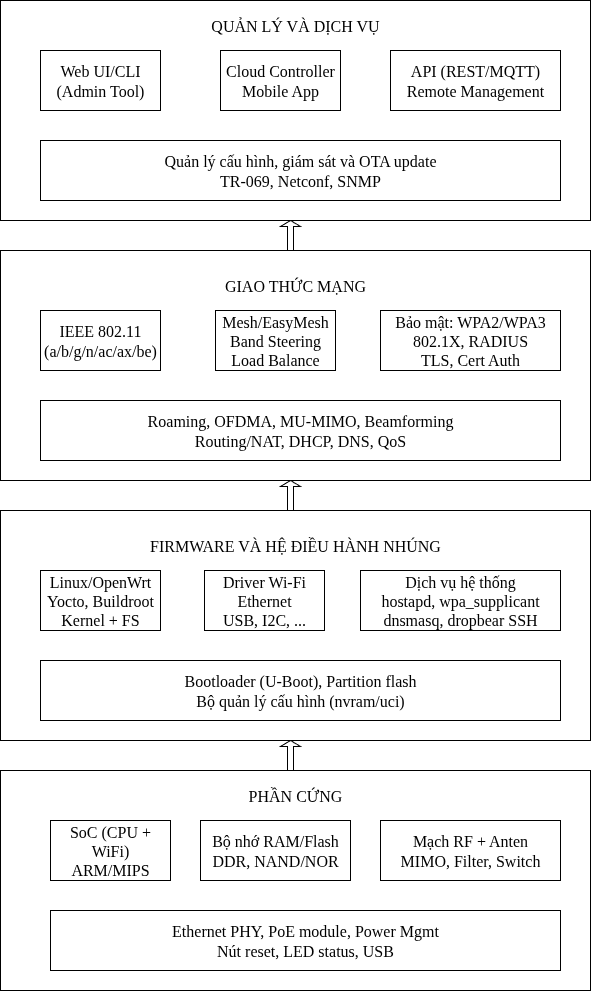
To design a system for software, you will need to combine knowledge in many areas not only programming, but also architectural thinking, project management and understanding user needs. If it is a complex hardware/software product such as Access Point (AP), the knowledge to design the system will be broader than pure software, because it must combine hardware, software, network, security and manufacturing techniques.
1. Hardware knowledge
1.1 Microprocessor and SoC architecture
- ARM, MIPS or specialized Wi-Fi chips (MediaTek, Qualcomm, Broadcom …).
1.2 Circuits and RF
PCB design, RF matching, antenna (omni, sector, MIMO).
Knowledge of frequency bands (2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz).
1.3 Hardware communication standards
- SPI, I²C, UART, PCIe, Ethernet PHY.
1.4 Power and energy management
PoE (Power over Ethernet) standard 802.3af/at/bt.
Protection against electric shock, anti-interference.
2. Knowledge of embedded systems
2.1 Embedded operating systems
- OpenWrt, Linux Embedded, Yocto, or custom firmware.
2.2 Device drivers
- Wi-Fi drivers (MAC, PHY), Ethernet, LED, push buttons, USB.
2.3 Limited memory and resource management
- Low RAM/Flash, weak CPU → optimize code and kernel configuration.
2.4 Bootloader
- U-Boot, firmware recovery mechanism, dual image.
3. Network and protocol knowledge
3.1 Wi-Fi standards
- IEEE 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac/ax (Wi-Fi 6/6E).
- OFDMA, MU-MIMO, Beamforming, DFS, CCA.
3.2 Mesh Networking
- EasyMesh, 802.11s, proprietary mesh protocols.
3.3 Connection management
- Roaming, band steering, load balancing.
3.4 Network security
- WPA2/WPA3, 802.1X, RADIUS, certificate-based authentication.
3.5 Remote administration
- TR-069, SNMP, Netconf, cloud controller.
4. System Software Knowledge
4.1 Configuration Management and CLI/Web UI
- Web admin (HTML/JS), command-line (BusyBox).
4.2 Background Services
- Hostapd, wpa_supplicant, dnsmasq, dropbear SSH.
4.3 API and Centralized Administration
- REST, MQTT, WebSocket for Controller.
4.4 Firmware Update Mechanism
- OTA (Over-the-Air), Brick Protection.
5. Testing and Optimization Knowledge
5.1 RF Testing
- Test transmit power, receive sensitivity, channel occupancy.
5.2 Network Performance
- Throughput, latency, jitter, QoS.
5.3 Load Capacity
- Multiple STAs (stations) simultaneously, stress testing.
5.4 Information security
- Penetration test, firmware security vulnerability test.
6. Manufacturing and certification process
6.1 Certifications and standards
- FCC, CE, RoHS, Wi-Fi Alliance.
6.2 Supply chain and BOM
- Component management, cost optimization.
6.3 Production line test
- Automatic RF, Ethernet, basic function testing before packaging.
Access Point system overview diagram
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.